TITANIC INQUIRY: THE GREATEST CIVIL MARITIME DISASTER IN HISTORY
The Titanic Inquiry would expose the greatest maritime disaster in history and be sure to raise government departments’ eyebrows and media across the world.
Although Titanic suffered a massive loss of life in 1912, the outcomes of both the British and American inquiry would in turn save thousands of lives for generations to come.
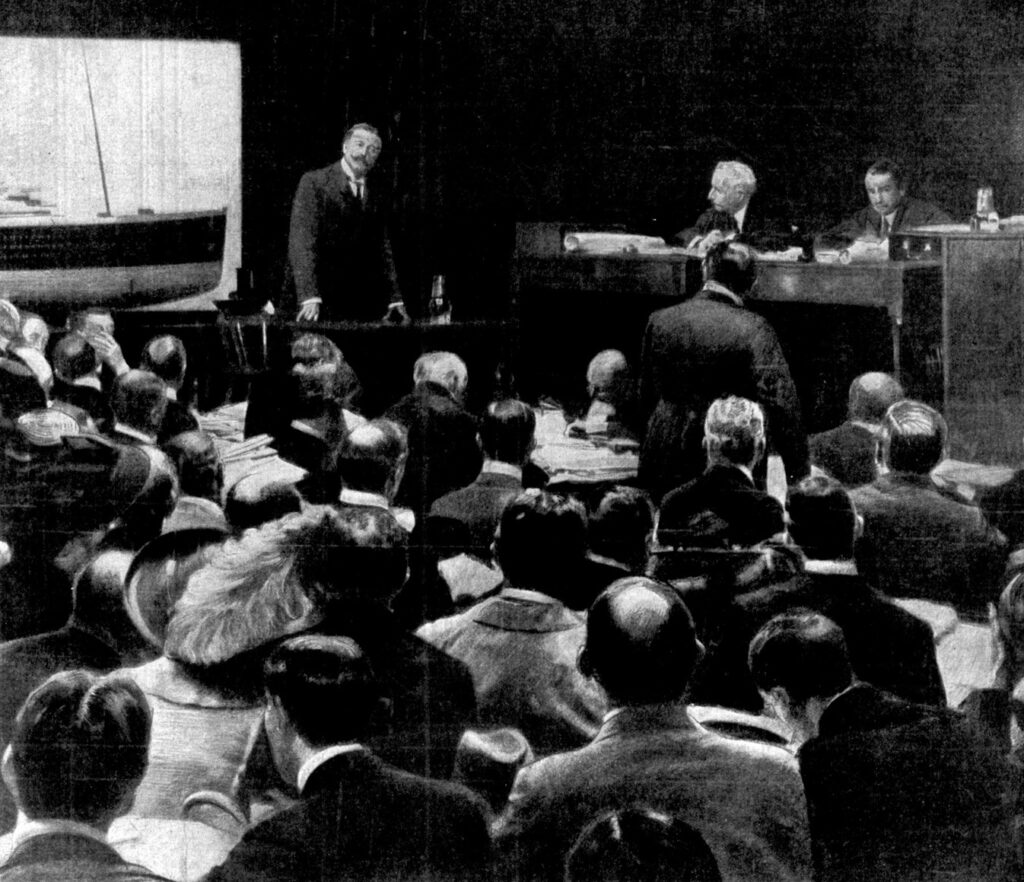
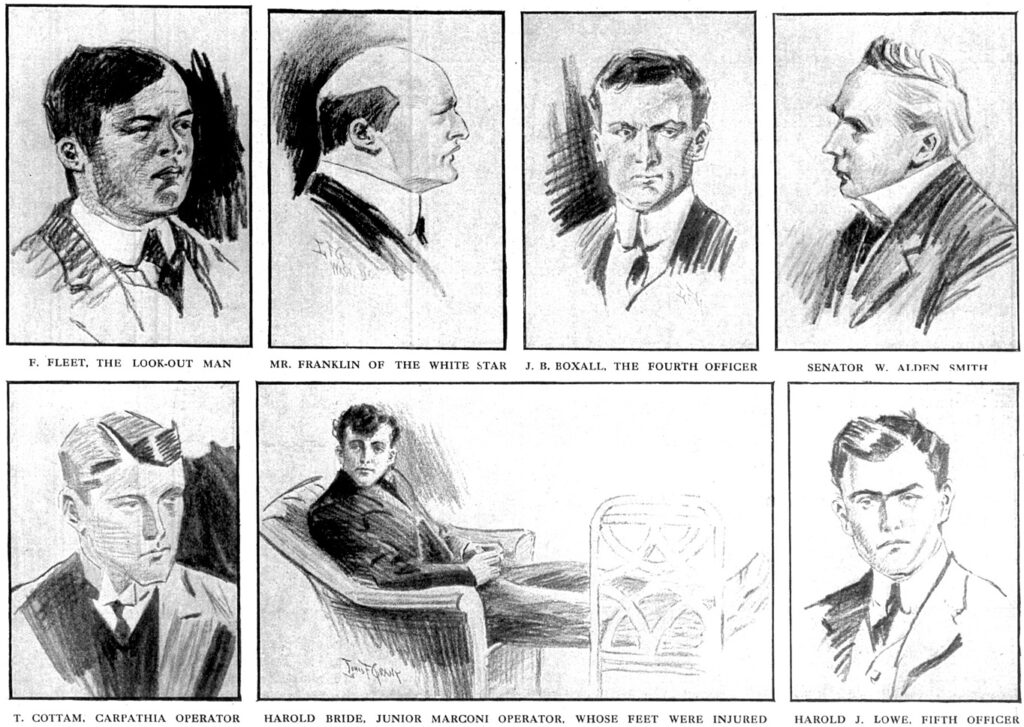
Senator William Alden Smith

Senator William Alden Smith, the American Inquiry, began at 10:30 the next morning after Carpathia arrived with its limited number of survivors. Senator William Alden Smith would lead the U.S inquiry and urgently got procedures underway before Titanic survivors left New York and could not be contacted again.
A Complete Titanic TEACHING UNIT
A complete unit of work to teach students about the historical and cultural impact Titanic made upon the world both back in the early 20th century. This complete unit includes.
“Overconfidence seems to have dulled the faculties usually so alert.”
— Senator Smith, on Captain E.J. Smith.
J.B Ismay was issued a summons immediately upon arriving on American soil but when he was grilled by Smith and the U.S Senate inquiry he played his cards very close to his chest claiming to be no more than a passenger of Titanic and claiming to have little to no intimate knowledge of the events that led to her demise.

“What do you think I am? Do you believe that I’m the sort that would have left that ship as long as there were any women and children on board? That’s the thing that hurts, and it hurts all the more because it is so false and baseless. I have searched my mind with deepest care, I have thought long over each single incident that I could recall of that wreck. I’m sure that nothing wrong was done; that I did nothing that I should not have done. My conscience is clear and I have not been a lenient judge of my own acts.”
— -J. Bruce Ismay, Director of the White Star Line
Although The American Inquiry would prove to be far more thorough and genuine than the subsequent British Inquiry it did little to lay blame or find answers for the American public who had suffered the loss of so many of their own citizens.
Many surviving White Star employees who testified refused to blame their superior and now deceased colleagues simply conceding that the events leading to Titanic’s demise were just sheer bad fortune.
Possibly the largest point of confusion was surrounding the Leyland steamer Californian. At only 19 miles away from Titanic, it was well within visible and radio contact before and during Titanic’s sinking yet for several inexplicable reasons could not make coherent communication with Titanic which surely would have saved hundreds of more lives and changed history.
The outcomes of the United States inquiry were mixed. Ismay and all crew were allowed to return home without any blame for Titanic’s sinking. From then on, all passenger ships must carry enough lifeboats to accommodate everyone on board, and crew must be well trained in their deployment use.

Secondly, steamers must carry searchlights and have a manned radio 24 hours of the day. These recommendations took effect almost immediately.
The Chief issue of concern from the British inquiry was the navigational negligence of Titanic. She sailed under full steam through ice infested waters which upon reflection seemed utter madness on behalf of Captain Smith. Questions were raised about whether Ismay the owner of White Star lines had forced Captain Smith to this speed to receive plaudits for the speed of Titanic as well as its elegance.
Secondly, was the Titanic structurally seaworthy? For such a mammoth ship, Titanic sank rapidly, which greatly affected the number of survivors that Carpathia collected.
The third issue of contention was the lack of lifeboats onboard Titanic. She could not provide a chance at survival for nearly half her passengers.
Beyond these three major issues, there was concern over staff and passengers’ behaviour onboard Titanic regarding the treatment of third-class passengers and lifeboat access equity.
The British Board of Trade’s inquiry seemed to be somewhat of a scam to appease the British public and media more so than trying to find genuine answers and lay blame upon anyone.
Essentially The Board of Trade was investigating itself, and it created all parameters that allowed Titanic to perish so easily. It seemed to have no intention to blame anyone for the disaster as it would spell disaster for British shipping and possibly pave the way for mammoth lawsuits filed against it.
The British investigation essentially concluded unsurprisingly without any blame laid upon White Star Lines and the British Board of Trade.
For a complete record of both the United States and British Inquiry, please visit the Titanic Inquiry Project. This site contains all transcripts and outcomes in complete detail.

The outcomes of the United States inquiry were mixed. Ismay and all crew were allowed to return home without any blame for Titanic’s sinking. From then on, all passenger ships must carry enough lifeboats to accommodate everyone on board, and crew must be well trained in their deployment use.
Secondly, steamers must carry searchlights and have an operated radio 24 hours of the day. These recommendations took effect almost immediately.
The Chief issue of concern from the British inquiry was the navigational negligence of Titanic. She sailed under full steam through ice infested waters which upon reflection seemed utter madness on behalf of Captain Smith. Questions were raised about whether Ismay the owner of White Star lines had forced Captain Smith to this speed to receive plaudits for the speed of Titanic as well as it’s elegance.
Secondly, was the Titanic structurally seaworthy? For such a mammoth ship, Titanic sank rapidly, which greatly affected the number of survivors that Carpathia collected.
The third issue of contention was the lack of lifeboats onboard Titanic. She could not provide a chance at survival for nearly half her passengers.
Beyond these three major issues, there was concern over staff and passengers’ behaviour onboard Titanic regarding the treatment of third-class passengers and lifeboat access equity.
The British Board of Trade’s inquiry seemed to be somewhat of a scam to appease the British public and media more so than trying to find genuine answers and lay blame upon anyone.
Essentially The Board of Trade was investigating itself, and it created all parameters that allowed Titanic to perish so easily. It seemed to have no intention to blame anyone for the disaster as it would spell disaster for British shipping and possibly pave the way for mammoth lawsuits filed against it.
The British investigation essentially concluded unsurprisingly without blaming White Star Lines and the British Board of Trade.
For a complete record of both the United States and British Inquiry, please visit the Titanic Inquiry Project. This site contains all transcripts and outcomes in complete detail.